About Us
|
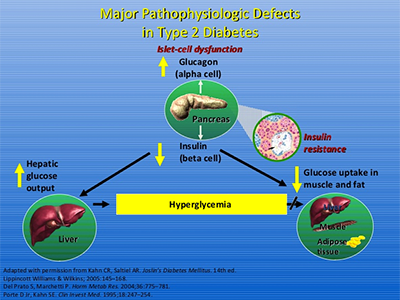
Type 2 diabetes is a progressive inflammatory disease. It is characterized by insulin resistance and pancreatic beta cell failure. Elevated fasting glucose levels, impaired glucose tolerance, and impairment of the first and the second phase of glucose-dependent insulin secretion (GDIS) are hallmarks of the disease. Inflammation-triggered deterioration of pancreatic beta cell function compromises their inherent capacity to compensate for insulin resistance. Pro-inflammatory signals originating from the activation of immune dysregulation, Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) and Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) contribute to the reduction in the beta-cell mass and consequential state of insulin dependence. There is a direct cause and effect relationship between the elevation of Prostaglandin E2 and inhibition of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) as well as destruction of beta cells. Functional response of beta cells and insulin sensitivity of insulin-responsive tissues such as liver, fat and skeletal muscle are tightly regulated by a feedback loop. This feedback loop determines the normal regulation of glucose metabolism by adjusting the glucagon-insulin molar ratio. There is a direct correlation between the magnitude of beta cells response and sensitivity of insulin-responsive tissues to insulin. As tissues develop insulin resistance, beta cells compensate with an increased output of insulin. Blood glucose levels rise in the presence of insulin resistance when beta cells are incapable of releasing sufficient insulin due to progressive deterioration of beta cell function. If pro-inflammatory signals are not blocked with the right combination of drugs, there will be progressive reduction in pancreatic beta cell mass due to inflammation-triggered apoptosis which leads to an irreversible state of pancreatic beta cell failure, a stage at which Type 2 diabetes becomes indistinguishable from Type 1 diabetes. The only treatment option available to patients at that stage is insulin therapy.
|
Click to Enlarge
|

Click to Enlarge
|
In spite of intense mono- and combination therapies with the existing modalities, patients experience deterioration of metabolic control of glucose homeostasis which is indicative of progressive deterioration of beta cell function. ARKAY is committed to filling clinically the most important gap that exists in the modalities used for the treatment options by targeting multiple distinct and overlapping mechanisms along the immune dysregulation-inflammation-insulin resistance axis that contribute to beta cell dysfunction. The complex etiology of Type 2 diabetes involves impairment of function of a variety of cell types that contribute to deterioration of beta cell function which triggers insulin resistance. ARKAY is advancing an innovative and novel anti-inflammatory 'Beta-cell-centric' platform that treats beta-cell dysfunction and maintains its inherent capacity to compensate for insulin resistance.
Dr. Stan Schwartz, MD, ARKAY's medical advisor described the 'Egregious Eleven' pathways and defects that contribute to hyperglycemia in his 'Beta-cell-centric' construct with beta-cell damage as the FINAL COMMON DENOMINATOR (Diabetes Care 2016; 39:179-186). To provide long-term sustainable glycemic control, the ideal therapeutic option has to favorably modulate maximum number of the 'Egregious Eleven' pathways with a minimum number of drugs that are safe for chronic use in the early stages of progressive deterioration of beta-cell function soon after a patient is diagnosed for Prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes when pancreas still contains a restorable critical mass of beta cells.
|
Our product blocks multiple signaling pathways and contribute to long-term sustainable glycemic control, prevent or delay the initiation of insulin therapy as well as prevent, delay or reduce the severity of diabetes-related complications. More importantly, It is expected to prevent primary and secondary failure of Metformin, the current standard of care. ARKAY's scientific rationale and the product concept is supported further by the consensus opinion of experts of the ADA, AACE, EASD and JDRF which highlighted the importance of targeting inflammation-mediated beta-cell destruction, progressive deterioration of beta-cell function and emphasized their role in the natural history of the pathophysiology of diabetes (Skyler, J.S. et al. 2017; Diabetes 66: 241-255).